 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Underground parking for 184 cars at Revolution Square in Moscow
Underground parking for 184 cars at Revolution Square in Moscow
The underground parking at Revolution Square is situated between Hotel Moskva and the former Lenin Museum close to collector of Neglinka River. Under the parking there are two subway line tunnels, 5 and 10 meter below its foundation slab.
Architectural and layout solution of the underground parking for 184 cars was developed by Workshop 11 of Mosproject-2 design institute and it includes a four-level car parking, an access ramp and servicing premises unit, which are interconnected via pedestrian tunnel with Trade and Recreation complex "Okhotny Ryad" at Manege Square. (DWF-drawing, 42.5 Kb)
















|
 |

Geological composition at this site was represented by:
6-8 m layer of fill-up soil with remains of old building foundations;
4-6 m layer of alluvial deposits of loam, sand and sandy loam lenses;
3-5 m layer of Izmailovsky limestone, eroded to size of crushed stone, gruss and dust with clayey aggregate, covering clay lenses and coarse grain fragments underlaying in certain areas of significantly fissured limestone and dolomite;
4-5 m layer of Meshcherensky marly-clay;
9-10 m layer of Perkhurovsky fissured limestone;
6-8 m layer of Neverovsky marly-clay.
Construction of underground parking at Revolution Square was executed in the area of influence of upper ground water horizon above the layer of alluvial sandy-clays and loam and gravity flow water horizon dating back to Izmailovsky eroded limestone.
In-situ reinforced concrete lining (DWF-drawing, 13.7 Kb) of underground parking including:
diaphragm walls and walls from bored-secant piles used as enclosing structures at construction stage and as bearing structures at operation stage;
sloping single-span roof vault, rigidly connected with walls by rebar outlets and having developed feet, hinge-resting on inner surfaces of walls and vault lying below;
sloping single-span vaults, each having developed feet, hinge-resting on inner surfaces of walls and on vault lying below (the lowest vault rests on foundation slab);
foundation slab (as reverse sloping vault), hinge connected with walls and vault-slab above.
The geometric shape of the vaults was designed in a way as to use in their concreting the unified knockdown metal formworks with plywood decking. Inner radiuses of vaults were selected in a manner as to exclude any "visual break" lines on their surface (the joining curves of different radius had common tangent line).
Vaults geometry differed from curved form geometry by estimated value of vaults deformation due to own weight, constant and temporal long-lasting loads: during concreting the vault copied curved form geometry and after stripping of forms - the designed geometry. The value of applied construction lift in crown - 50 mm.
By means of increased thickness of roof vault and making its top by 1% slope to the walls the required load-bearing capacity was achieved (higher compared to floor vaults).
All the vaults were reinforced by spatial reinforcing cages that were assembled in specially made conductors right at construction site of factory-made bent parts. Regular bar reinforcement of А-III and A-I class was used. Basic cages width were - 2.4 m.
In assembling of vaults reinforcement the welded joints between reinforcing cages were not designed. Joints between reinforcing cages were made in zones of practically zero bending moments by overlapping double loop-shaped rebar outlets and installing inside them longitudinal distributing bars.
Diaphragm walls as well as bored-secant walls of the lining were made of В25 concrete, vaults and foundation slab - В30 concrete.
Waterproofing of foundation slab and walls was made as continuous using rolled bituminous material "Isoplast P", thickness 4 mm. Joint points of the foundation slab with diaphragm walls in grooves were additionally strengthened with "Isolene" layer - reinforced light-stabilized polyethylene. Waterproofing of roof vault was made of bentomats based on geotextile material "Voltex" and sodium bentonite "Volclay".
Publications…
Construction of underground parking was executed by open method under protection of temporary metal three-tier support in the following sequence (DWF-drawing, 23.9 Kb):
execution of pit enclosure (diaphragm walls, thickness 90 cm and walls made of bored-secant piles diameter 83 cm);
tier-by-tier soil excavation in pit with temporary metal support installed (doubled I-beam belts №55B1 and pipe buntons, diameter 630х8 mm and spacing 5 m);
execution of concrete bad, waterproofing of foundation slab by one layer of "Isoplast P";
|
concreting of foundation slab;
dismantling temporary metal support of the lower tier;
waterproofing of diaphragm walls of the pit enclosures by one layer of "Isoplast P" at -4 floor;
concreting of floor vault at -4 floor;
stripping of form and installation props under vault at -4 floor;
dismantling of temporary metal support of the intermediate tier;
waterproofing of diaphragm walls of the pit enclosures at -3 floor;
concreting of floor vault at -3 floor;
stripping of form and installation props under vault at -3 floor;
dismantling of temporary metal support of the upper tier;
waterproofing of diaphragm walls of the pit enclosures at -2 floor;
concreting of floor vault at -2 floor;
stripping of form and installation props under vault at -2 floor;
waterproofing of diaphragm walls up to their top;
concreting of roof vault;
waterproofing, thermal insulation of roof vault, back filling of car parking and territory landscaping.
The execution of works on underground car parking was carried out from an access ramp towards Manezhnaya Square, because right on construction critical path there was an underground construction of pedestrian connecting tunnel in progress.
At construction stage the ramp walls was executed as open shaft of inner diameter about 24 m using 83 cm diameter bored-secant piles with spacing 65 cm. The ramp exit structure was made as in-situ reinforced concrete serpentine resting on clamp-type wall of shaft waterproofing, pylons along inner circle and the wall of cylindrical staircase shaft.
Concreting of floor vaults and roof vault was executed for entire span 17.5 m at one go practically at several floors at an average rate of 90-100 running meter (or not less than 990-1100 m3) per month.
Construction of four levels vaulted lining of underground parking at Revolution Square features the following parameters:
 concrete consumption for lining - 86.5 m3/m;
concrete consumption for lining - 86.5 m3/m;
reinforcing steel consumption for lining - 11.1 t/run.m;
concrete consumption for one floor vault - 11 m3/run.m;
reinforcing steel consumption for floor vault - 156 kg/m3;
concrete consumption for roof vault - 15.7 m3/run.m;
reinforcing steel consumption for roof vault - 169 kg/m3.
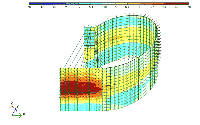
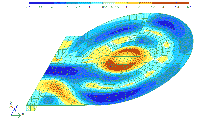
The designing of such lining as well as economy designing of entire underground parking would not be feasible without making sophisticated computer calculations with respect to re-distribution of stresses and deformations in the bearing structures in construction process and at operation stage.
Publications…
Patents…
Drawings catalogue…
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Copyright © 2001-2022 "Yurkevich Engineering Bureau Ltd." / All Rights Reserved
|
|
|